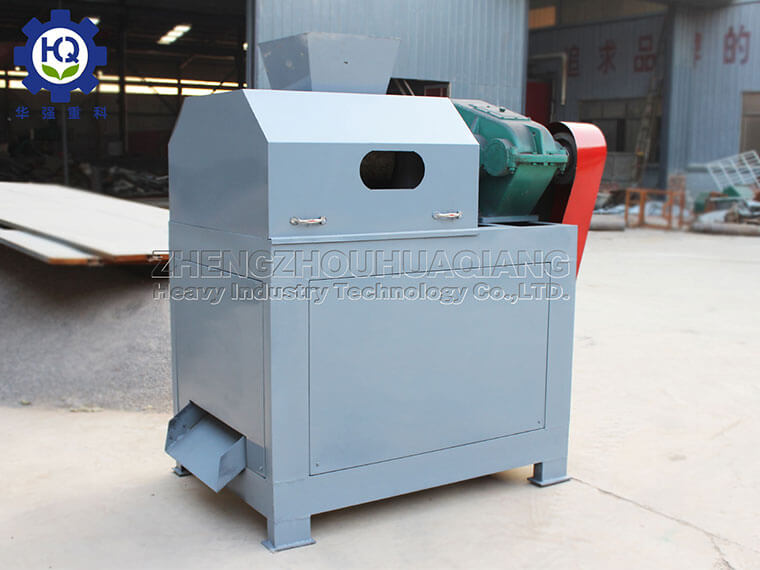
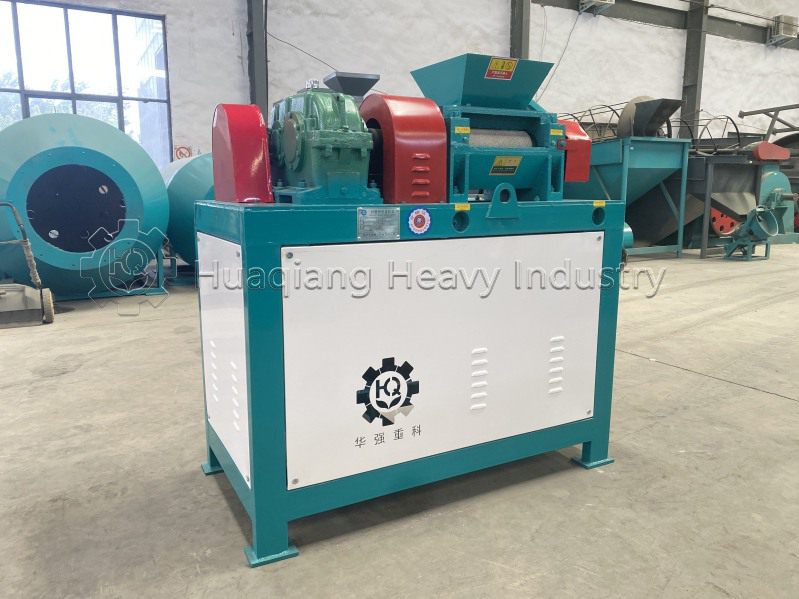
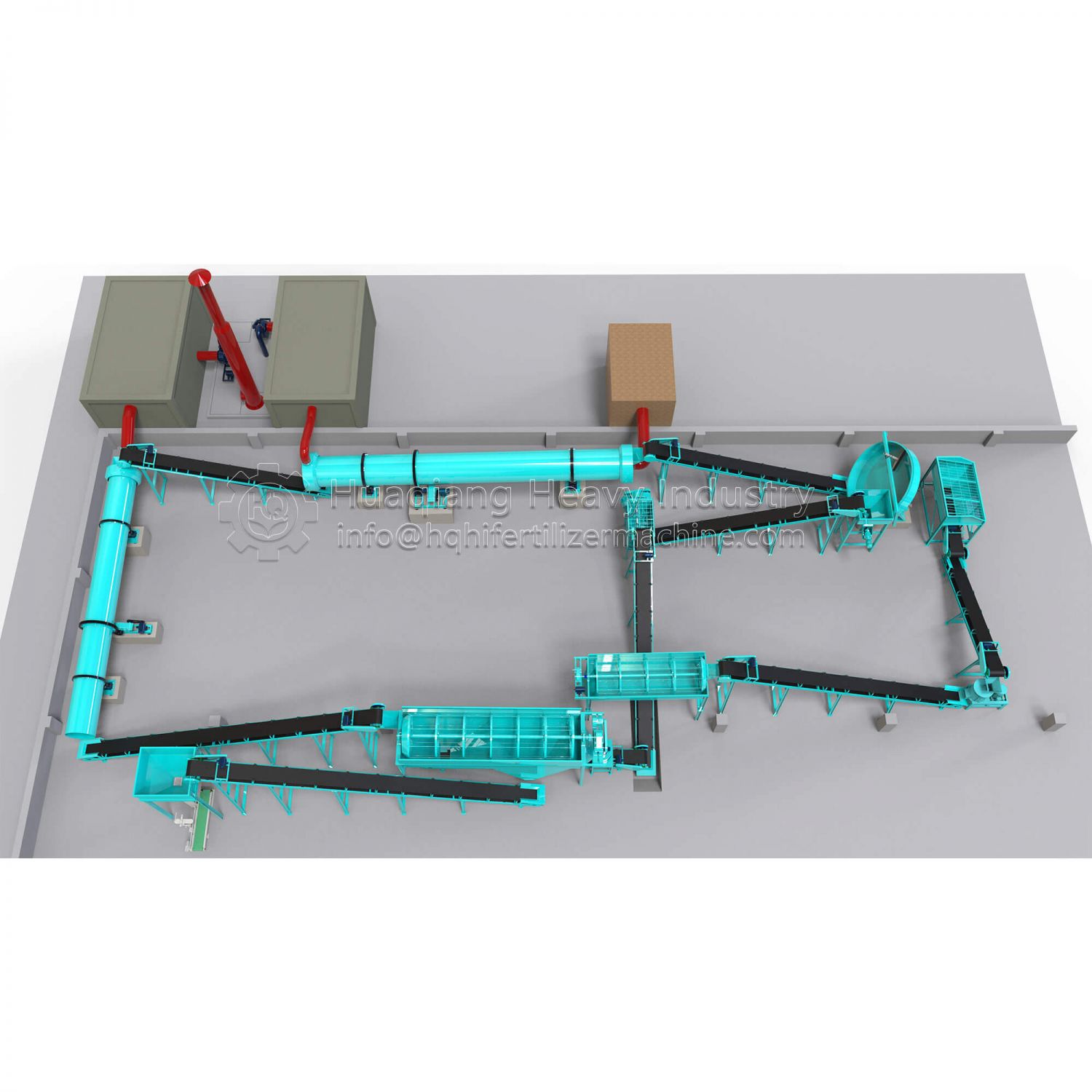
Organic fertilizer equipment is a key tool for producing organic fertilizers, which can be classified into various types based on their functions and uses. These devices are widely used in agriculture, horticulture, forestry and other fields, promoting the development of the organic fertilizer industry..jpg)
Category:
Fermentation equipment: such as organic fertilizer turntables and fermentation tanks, used for aerobic fermentation of materials.
Crushing equipment: such as organic fertilizer crusher, which crushes the fermented material to the appropriate particle size.
Granulation equipment: such as organic fertilizer granulators, which turn crushed materials into granules.
Drying equipment: such as organic fertilizer dryer to reduce particle moisture.
Cooling equipment: such as organic fertilizer cooling machine, to reduce particle temperature.
Screening equipment: such as organic fertilizer vibrating screen, to remove unqualified particles.
Packaging equipment: such as automatic packaging machines, which package finished products before leaving the factory.
Application areas:
Agriculture: used for producing organic fertilizers, biological fertilizers, compound fertilizers, etc., to improve crop yield and quality.
Horticulture: Used for producing specialized fertilizers for flowers and vegetables to promote plant growth.
Forestry: Used for producing specialized fertilizers for forest trees to promote their growth.
Ecological restoration: used for producing specialized fertilizers for ecological restoration and improving soil environment.
Case analysis:
After introducing organic fertilizer equipment, a certain organic fertilizer production enterprise saw a 30% increase in production efficiency, a 20% increase in product qualification rate, and a significant increase in market share.
Conclusion:
Organic fertilizer equipment has diversified its classification and application fields, meeting different production needs and promoting the development of the organic fertilizer industry. By selecting and using organic fertilizer equipment reasonably, production efficiency and product quality can be improved, promoting sustainable agricultural development.
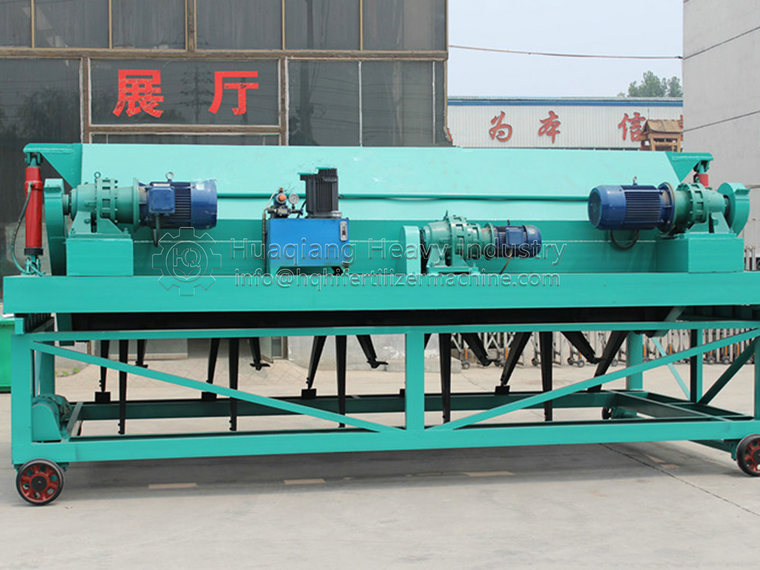




.jpg)


